Complete Guide for Mobile Advertising: What It Is, How It Works, and Why It Matters

Table of content
What is Mobile Advertising?
Common Ad Formats & Pricing Models
Main Objectives of Mobile Advertising Campaigns
How Does Mobile Advertising Work?
Advantages of Mobile Advertising
Strategies for Scalable Mobile Campaign Growth
Privacy and Mobile Advertising: Compliance and User Respect
Conclusion: Mobile Is Much More Than Banners
FAQ
With the continuous rise in mobile device usage and traditional channels struggling to sustain growth, mobile advertising has become a crucial performance channel for app-based businesses.
Global mobile advertising in 2025 is valued between $228 billion and $447 billion, with mobile accounting for roughly 56–70% of total digital ad spending worldwide. Growth remains strong, with the mobile advertising market increasing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 10–21% over recent years and projected to continue this trajectory through the decade
But what exactly is mobile advertising? This guide covers the fundamentals — from ad formats and monetization models to privacy-safe solutions like OEM advertising.
What is Mobile Advertising?
Mobile advertising is the strategic promotion of apps, products, and services through ads displayed on smartphones and tablets. These ads are seamlessly integrated across various mobile environments such as apps, mobile browsers, interactive games, and social networks.
What sets mobile advertising apart from traditional digital campaigns is its hyper-targeting capability. By combining data like location, in-app behavior, and events (such as purchases or sign-ups), advertisers can create highly personalized campaigns.
Additionally, the mobile environment enables real-time delivery, context-based personalization, and highly interactive formats.
Common Ad Formats & Pricing Models
Mobile ads now come in high-impact, story-driven formats designed to reach users at critical moments in their device journey.
Here are the most common:
| Format | Key Goal | Pricing Model |
| Banner Ads | Awareness / Traffic | CPC / CPM |
| Interstitial Ads | Mid‑funnel engagement | CPC / CPA |
| Rewarded Video Ads | Retention / Loyalty | CPV / CPA |
| Native Ads | Seamless UX, brand fit | CPC / CPM |
| Playable Ads | Drive installs | CPI / CPA |
| Short‑form (UGC style) | Emotional/viral impact | CPV / CPA |
💡 Tip: Early-stage or pre-launch apps can leverage OEM advertising — a channel that guarantees constant exposure via branded folders, push notifications, and pre-installations. These formats are delivered directly on smartphones’ interfaces without relying on cookies or tracking IDs.
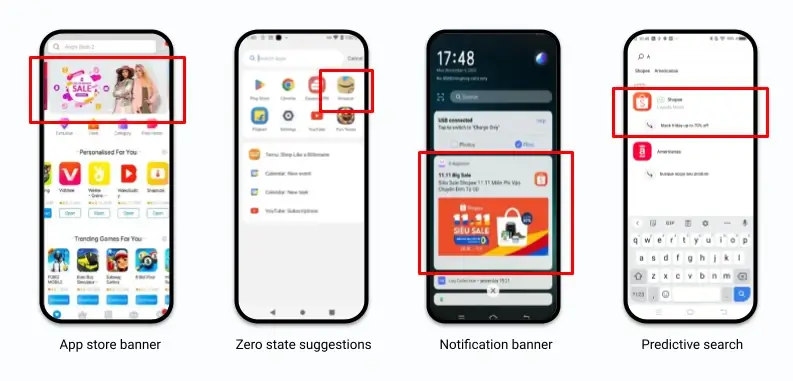
Pricing Models Recap:
- CPI (Cost Per Install): Payment per app installation
- CPA (Cost Per Action): Payment for specific actions (e.g., registration, purchase)
- CPC (Cost Per Click): Payment per click, regardless of conversion
- CPV (Cost Per View): Payment per video view
These models offer flexibility for brands to choose the most effective strategy based on their goals and campaign maturity.
Main Objectives of Mobile Advertising Campaigns
As smartphone and tablet use grow, it’s essential for brands to reach consumers where they spend most of their time. Campaigns can be designed with various objectives aligned to business stage and audience profile. Understanding these goals is the first step to building effective, measurable strategies. Common goals include:
- Brand Awareness: Expand visibility and recognition among a broad audience.
- Lead Generation: Collect potential customer contacts for future marketing efforts.
- Sales Growth: Drive purchases through promotions, discounts, and exclusive offers.
- Traffic Driving: Direct users to websites or apps to explore products, buy, or engage with content.
- Engagement Promotion: Encourage user interaction via likes, comments, and shares.
- Customer Loyalty: Keep customers engaged through personalized experiences and loyalty programs.
- App Installs and Usage: Boost app downloads and active usage.
- Customer Relationship: Establish direct communication channels, offering support and personalized service.
- Event or Product Launch Promotion: Promote events or new products/services through targeted campaigns.
Without clear, measurable goals, it’s impossible to optimize campaigns, adjust strategies, or ensure expected ROI. Continuous data analysis allows companies to adapt quickly to consumer behavior and market changes, maximizing their mobile marketing outcomes.
📊 Common KPIs:
KPIs vary depending on campaign goals (acquisition, engagement, retention, monetization, etc.), but key metrics include:
- CPI (Cost Per Install)
- CPA (Cost Per Action)
- ROAS (Return on Ad Spend)
- LTV (Lifetime Value)
- Retention Rates (Day 1, Day 7, Day 30)
How Does Mobile Advertising Work?
A mobile campaign operates through a partnership among the advertiser (brand), a platform (ad network or attribution platform), and publishers (partners who display the ads).
The advertiser sets the goals, budget, and target audience. The media platform configures, segments, and delivers ads across various channels and formats. Finally, publishers promote the brand in their own environments, reaching users in real time.
The entire journey is monitored with KPIs like installs, engagement, retention, and ROI (ROAS), ensuring scalable, secure performance aligned with user privacy.
Roles explained:
- Advertiser:
The company or individual aiming to reach mobile users with goals such as acquiring new users, boosting engagement and retention, or generating revenue (purchases, subscriptions, ads). They define KPIs and choose pricing models like CPI, CPA, or CPC. - Ad Network or Platform:
Intermediaries connecting advertisers and publishers. They provide infrastructure to distribute ads across channels, measure performance, optimize delivery in real time, and integrate with MMPs (e.g., AppsFlyer, Adjust, Branch).
Some platforms, like Admitad’s Taprevo, specialize in OEM advertising with an SDK integrated into Android smartphones, using real-time behavioral data to gain audience insights and build personas from historical trends.

- Publisher (Media Partner):
Entities responsible for showing ads to end users, which can be apps (games, utilities), agencies or affiliates, influencers, social networks, messaging platforms (SMS, push, email), OEM partners, or specialized media networks. Publishers monetize their mobile traffic by integrating ad formats.
Advantages of Mobile Advertising
Mobile advertising is effective because it reaches users where they spend the most time: on their phones.
Key advantages include:
- 📱 Growing smartphone usage in developed and emerging markets
- 🎯 Precise targeting based on location and in-app behavior data
- 💰 Access to mobile-first audiences ideal for apps and digital brands
- ⚡ Real-time engagement directly on the user’s device
- 📊 Flexible cost models like CPI and CPA
- 🔒 Privacy compliance, with OEM channels that don’t rely on IDFA/GAID
Strategies for Scalable Mobile Campaign Growth
To achieve sustainable growth via mobile marketing, brands need to look beyond one-time installs and focus on user value over time. Effective strategies include:
- Diversify Channels: Don’t rely on a single traffic source. Combine OEM advertising, social media, influencers, and programmatic channels to reach users at multiple journey points.
- Optimize for Bottom-Funnel KPIs: Go beyond CPI and focus on in-app actions like purchases, sign-ups, and retention. CPA- or ROAS-based models work best.
- Leverage OEM Inventory: Native device media reaches high-intent users at scale, with less fraud and no auction competition.
- Run A/B Tests: Regularly test creatives and audience segments to identify top performers and improve results.
- Use Smart Automation: Employ AI-driven platforms for targeting, automated optimization, and fraud prevention.
- Focus on Retention and LTV: Acquiring users is just the start. Build strategies to maintain engagement and loyalty over time.
Privacy and Mobile Advertising: Compliance and User Respect
Modern mobile advertising is built on privacy-by-design principles. Rather than indiscriminately tracking users, campaigns comply with laws like LGPD, GDPR, and CCPA, respecting user rights regarding data use.
Ways to ensure this include:
- Explicit consent before collecting personal data
- Anonymized and aggregated data to protect identity
- Privacy-first technologies like Apple’s SKAdNetwork and Google’s Privacy Sandbox, enabling measurement and targeting without exposing sensitive data
- On-device contextual and behavioral targeting, with data processed locally without sharing personal info externally
Mobile ad formats — such as notifications, native cards, and subtle banners — are designed to be helpful and non-intrusive, preserving user experience.
Good mobile advertising respects users’ time, attention, and data, building trust and sustainable results for brands.
Conclusion: Mobile Is Much More Than Banners
Mobile advertising goes beyond banners: it involves advanced targeting, smart pricing models, and engaging formats to drive measurable growth.
With creative strategies, data-driven optimization, and a focus on real KPIs, it delivers scalable results for app developers, marketers, and affiliates.
FAQ
How to avoid fraud in mobile campaigns?
Work with trusted networks, use MMPs for attribution, monitor KPIs, and prefer channels with direct inventory like OEM.
Does mobile advertising harm user experience (UX)?
It depends on the format and delivery. Native or rewarded ads create less friction. A/B testing helps find the ideal balance.
What’s the difference between mobile and web advertising?
Mobile ads are optimized for smaller touch screens, offer geographic targeting, and real-time delivery.
What are OEM channels?
Advertising channels operated by device manufacturers (like Xiaomi, Samsung) that show ads directly in system interfaces — folders, notifications, native apps.
What pricing models exist?
CPI (install), CPA (action), CPC (click), CPV (view). Choose based on your goal.
Is mobile advertising privacy-compliant?
Yes, especially OEM channels that don’t use personal identifiers like IDFA or GAID, making them safe in post-ATT and GDPR environments.












